This 2005 Survey is an annual survey conducted by IDA to determine the level of infocomm usage among companies in Singapore
1
.
The sample was selected from the Establishment Sampling Frame maintained by the Department of Statistics (DOS). The sample was stratified by the Singapore Standard Classification of Industrial Codes. Fieldwork for the 2005 Survey was carried out from end-November 2005 to mid-February 2006.
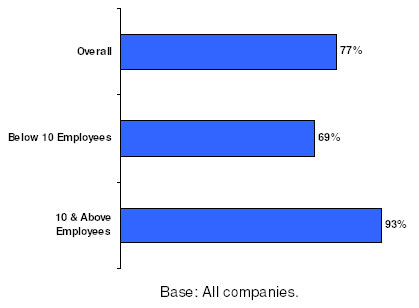
77% of companies used infocomm appliances
2
. The usage level is higher in companies with 10 or more employees at 93%.
Figure 1: Usage of Infocomm Appliances
The Internet continues to be a valuable tool for companies in Singapore; more so for the larger companies who also prefer broadband mode of access to the Internet.
-
71% of companies used Internet (Figure 2). The penetration rate is higher for companies with 10 or more employees (91%).
Figure 2: Usage of Internet
-
55% of companies used broadband Internet access (Figure 3). This usage level is higher in companies with 10 or more employees at 77%.
Figure 3: Usage of Broadband Internet Access
-
31% of companies used narrowband Internet access (Figure 4). This usage level is higher in companies with 10 or more employees at 40%.
Figure 4: Usage of Narrowband Internet Access
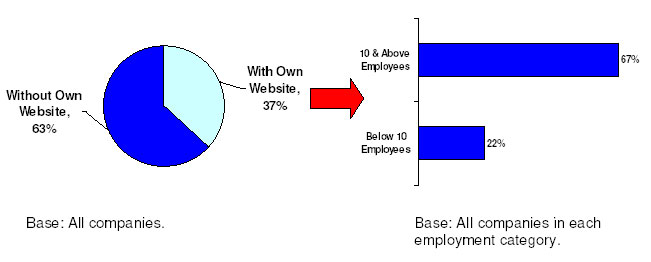
37% of companies in Singapore had their own website (Figure 5). 67% of companies with 10 or more employees had their own website as compared to 22% of companies with less than 10 employees.
Figure 5: Web Presence
There is not much difference between the types of Internet applications/ services used by companies with broadband Internet access and those with narrowband Internet access.
Generally, the usage of each Internet applications/service was higher for companies with broadband Internet access (Table 1).
Table 1: Top Ten Uses of Internet
|
|
Internet
|
Broadband Internet Access
|
Narrowband Internet Access
|
|
For sending or receiving mails
|
90%
|
88%
|
86%
|
|
For information search
|
88%
|
87%
|
81%
|
|
For banking and financial services
|
50%
|
53%
|
44%
|
|
For monitoring purposes
|
36%
|
39%
|
32%
|
|
For finding information about employment opportunities (recruitment and search)
|
35%
|
38%
|
29%
|
|
For marketing/promotion activities
|
34%
|
37%
|
27%
|
|
As a platform to deliver contents/services
|
32%
|
33%
|
26%
|
|
As a general communication tool excluding emails such as instant messaging
|
30%
|
33%
|
23%
|
|
For telecommuting/remote access
|
28%
|
32%
|
21%
|
|
To access collaborative tools (e.g. file sharing)
|
25%
|
28%
|
18%
|
Base: All companies with the different Internet access.
Table 2 lists the top five barriers to infocomm usage, as ranked by survey respondents based on the significance of each of the barriers listed below.
Table 2: Top Five Barriers to Infocomm Usage
|
Infocomm expenditure is too high
|
1
|
|
New versions of existing software are introduced too often
|
2
|
|
The level of infocomm skills is too low among the employed personnel
|
3
|
|
Lack of perceived benefits
|
4
|
|
Supply of infocomm technology is not matching the infocomm needs of the organisation
|
5
|
Base: All companies without any infocomm appliances.
Table 3 lists the top five barriers to the usage of Internet, as ranked by survey respondents based on the significance of each of the barriers listed below.
Table 3: Top Five Barriers to Usage of Internet
|
Security concerns (e.g. hacking and viruses)
|
1
|
|
Expenses for development and maintenance of web sites are too high
|
2
|
|
Technology is too complicated
|
3
|
|
Data communications expenses are too high
|
4
|
|
Losses in amount of working time because of time spent on irrelevant surfing
|
5
|
Base: All companies which did not use Internet.
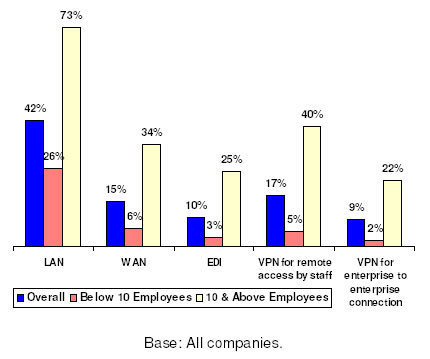
LAN
4
had traditionally been one of the most commonly used infocomm network technologies. In 2005, 42% of companies used LAN; 17% of companies used VPN
5
for remote access by staff; and 9% used VPN for enterprise to enterprise connection (Figure 6). Usage of all infocomm network technologies was higher for companies with 10 or more employees.
Figure 6: Usage of Infocomm Network Technologies
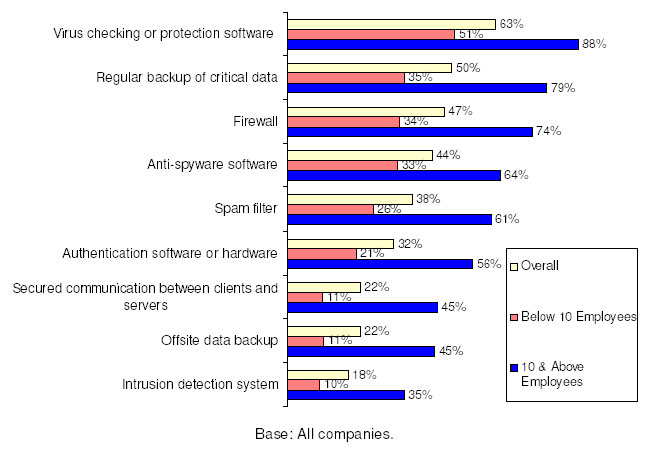
Virus checking or protection software was the most popular infocomm security measure among companies (Figure 7). Usage of all infocomm security measures was higher for companies with 10 or more employees.
Figure 7: Usage of Infocomm Security Measures
1
Unlike earlier IDA infocomm usage surveys, the 2005 Survey was based on a different methodology and classifications so as to align with benchmarked best practices. Hence, figures are not always comparable with those published in earlier infocomm usage survey reports. In particular, the revision in the methodology resulted in slightly lower figures than those reported in earlier infocomm usage survey reports.
2
With reference to usage of personal computers, laptops, workstations or terminals, and usage of wireless Internet on mobile phones/personal digital assistants.
3
A company can have both broadband and narrowband Internet access. Each column therefore has a different base of companies.
4
LAN refers to Local Area Network/Intranet within a company.
5
VPN refers to Virtual Private Network.
WAN refers to Wide Area Network/Extranet between a company and other companies. EDI refers to Electronic Data Interchange including web-enabled EDI. 9
